PHOTOVOLTAICO vs VVF

UNI 9177

ALL ABOUT PV FIRE PREVENTION
Legislative Decree No. 144 of September 23, 2022 (Official Gazette No. 223 of September 23, 2022), in Article 16 of Fire Prevention Procedures, establishes that, following the ongoing energy emergency, in order to facilitate the installation of photovoltaic and solar thermal systems on the roofs and facades of buildings serving activities subject to fire prevention inspections for the assessment of complete project documentation, if required after installation, the deadlines are reduced from 60 to 30 days until December 31, 2024.

WORSENING IF:
Photovoltaic systems are not among the activities subject to fire prevention controls pursuant to Presidential Decree no. 151 of August 1, 2011, "Regulation simplifying the rules governing fire prevention procedures, pursuant to Article 49, paragraph 4-quater, Legislative Decree no. 78 of May 31, 2010, converted with amendments by Law no. 122 of July 30, 2010." Generally speaking, the installation of a photovoltaic (PV) system, depending on its electrical/construction characteristics and/or installation methods, may increase the existing fire risk. For the building served, this increase could result in: - interference with the combustion product ventilation system (partial/total obstruction of translucent elements, impediments to the opening of exhaust vents); - obstruction to the cooling/extinguishing operations of combustible roofs; - risk of flames spreading outside or inside the building (presence of pipes on the roof of a building divided into multiple compartments - change in the speed of fire spread in a single-compartment building). NO ASSURANCE IF: The installation must be carried out in such a way as to prevent the spread of a fire from the photovoltaic generator to the building in which it is incorporated. This condition is considered met if the photovoltaic system, incorporated into a construction project, is installed on non-combustible roofing and/or façade structures and elements (Class 0 according to Ministerial Decree 26/06/1984 or Class A1 according to Ministerial Decree 10/03/2005). It is also equivalent to place a layer of fire-resistant material of at least El 30 and non-combustible (Class 0 according to Ministerial Decree 26/06/1984 or Class A1 according to Ministerial Decree 10/03/2005) between the photovoltaic modules and the support surface.
PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS - FIRE PREVENTION REGULATIONS
Don't despair, there's a solution to everything... maybe!!! Download the attached document.
Installazione impianti fotovoltaici (da 07/02/2012)
in attività soggette al DPR151
SCIA con dichiarazione di non aggravio

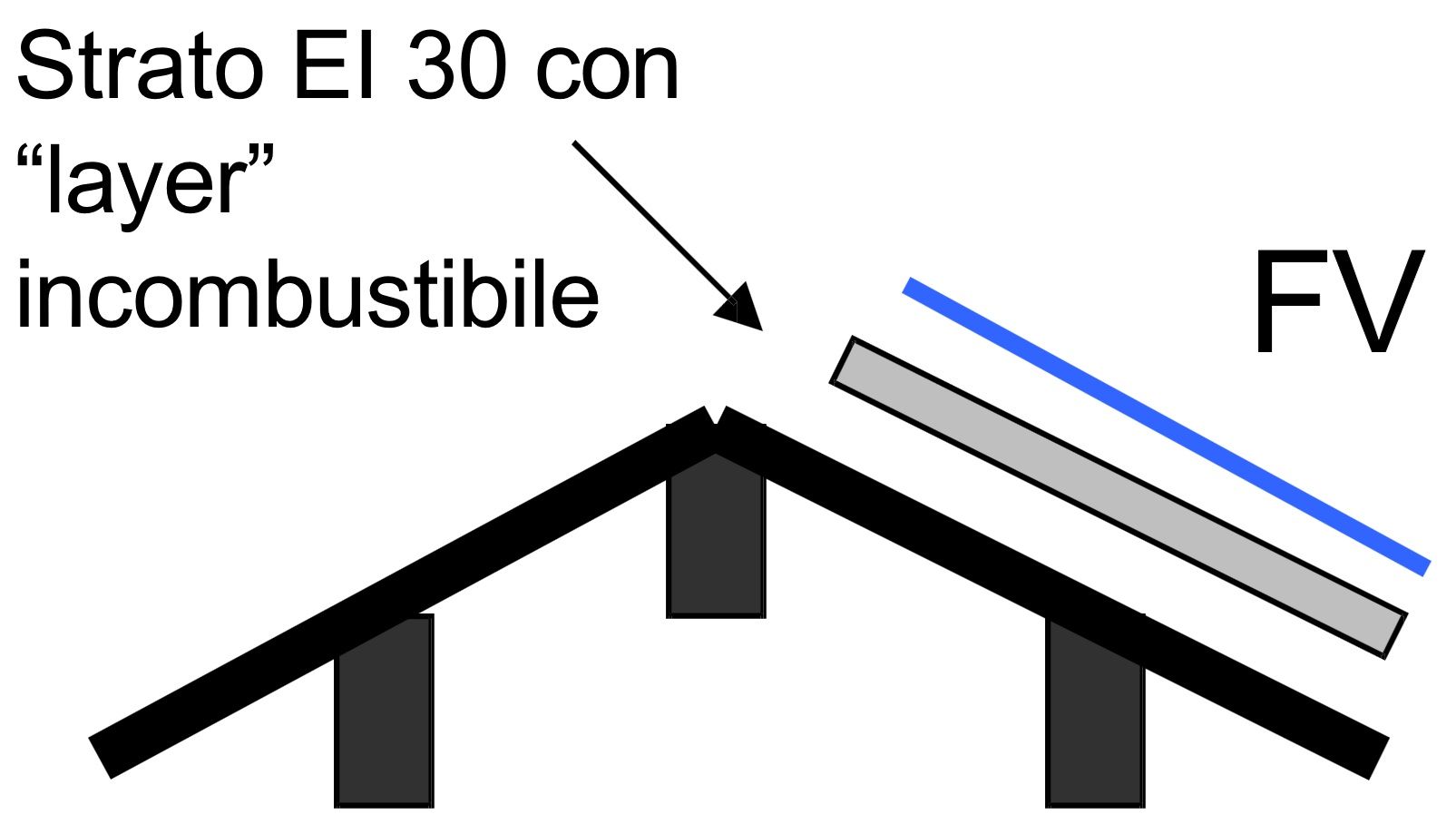
BORDER LINE SITUATIONS - WHERE TO INSTALL AN EI30 LAYER








